List of Schedule III drugs (US) This is the list of Schedule III drugs as defined by the United States Controlled Substances Act at 21 U.S.C. § 812 (c) and 21 CFR 1308.13, with modifications through August 22, 2014 (79 FR 49961 ). The following findings are required for drugs to be placed in this schedule. Schedule III drugs abuse potential is less than Schedule I and Schedule II drugs but more than Schedule IV. Some examples of Schedule III drugs are: Products containing less than 90 milligrams of codeine per dosage unit (Tylenol with codeine), ketamine, anabolic steroids, testosterone.
Editor-In-Chief:C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D.[1]
Overview
This is a list of Schedule III drugs under the Controlled Substances Act for the United States.Required findings for drugs to be placed in this schedule: [1]
- The drug or other substance has a potential for abuse less than the drugs or other substances in schedules I and II.
- The drug or other substance has a currently accepted medical use in treatment in the United States.
- Abuse of the drug or other substance may lead to moderate or low physical dependence or high psychological dependence.
The complete list of Schedule III drugs are as follows. [2] The Administrative Controlled Substances Code Number for each drug is included.
Stimulants
| ACSCN | Drug |
|---|---|
| 1228 | Benzphetamine |
| 1645 | Chlorphentermine |
| 1647 | Clortermine |
| 1615 | Phendimetrazine |
Depressants
| ACSCN | Drug |
|---|---|
| 2126 | Amobarbital |
| 2100 | Any derivative of Barbituric acid |
| 2510 | Chlorhexadol |
| 2020 | Embutramide |
| 2012 | Gamma-Hydroxybutyric acid (for applications under section 505 of Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act) |
| 7285 | Ketamine |
| 7300 | Lysergic acid |
| 7310 | Lysergic acid amide |
| 2575 | Methyprylon |
| 2271 | Pentobarbital |
| 2316 | Secobarbital |
| 2600 | Sulfondiethylmethane |
| 2605 | Sulfonethylmethane |
| 2610 | Sulfonmethane |
| 7295 | Tiletamine and zolazepam |
Narcotics
| ACSCN | Drug |
|---|---|
| 9803 | Not more than 1.8 grams of codeine per 100 milliliters or not more than 90 milligrams per dosage unit, with an equal or greater quantity of an isoquinoline alkaloid of opium |
| 9804 | Not more than 1.8 grams of codeine per 100 milliliters or not more than 90 milligrams per dosage unit, with one or more active, nonnarcotic ingredients in recognized therapeutic amounts |
| 9805 | Not more than 300 milligrams of dihydrocodeinone (hydrocodone) per 100 milliliters or not more than 15 milligrams per dosage unit, with a fourfold or greater quantity of an isoquinoline alkaloid of opium |
| 9806 | Not more than 300 milligrams of dihydrocodeinone (hydrocodone) per 100 milliliters or not more than 15 milligrams per dosage unit, with one or more active nonnarcotic ingredients in recognized therapeutic amounts |
| 9807 | Not more than 1.8 grams of dihydrocodeine per 100 milliliters or not more than 90 milligrams per dosage unit, with one or more active nonnarcotic ingredients in recognized therapeutic amounts |
| 9808 | Not more than 300 milligrams of ethylmorphine per 100 milliliters or not more than 15 milligrams per dosage unit, with one or more active, nonnarcotic ingredients in recognized therapeutic amounts |
| 9809 | Not more than 500 milligrams of opium per 100 milliliters or per 100 grams or not more than 25 milligrams per dosage unit, with one or more active, nonnarcotic ingredients in recognized therapeutic amounts |
| 9810 | Not more than 50 milligrams of morphine per 100 milliliters or per 100 grams, with one or more active, nonnarcotic ingredients in recognized therapeutic amounts |
| 9064 | Buprenorphine |

Anabolic steroids
| ACSCN | Drug |
|---|---|
| 4000 | Anabolic steroids |
Hallucinogens

| ACSCN | Drug |
|---|---|
| 7369 | Dronabinol in sesame oil and encapsulated in a soft gelatin capsule |
References
- ↑Template:Uscsub retrieved October 2, 2007
- ↑http://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/21cfr/cfr/1308/1308_13.htm retrieved October 2, 2007
See also
Template:WikiDoc Sources
Marijuana
List of Controlled Substances
Lists of Scheduling Actions, Controlled Substances, Regulated Chemicals (PDF) (May 2021)
This document is a general reference and not a comprehensive list. This list describes the basic or parent chemical and does not describe the salts, isomers and salts of isomers, esters, ethers and derivatives which may also be controlled substances.
| Scheduling Actions | Controlled Substances | List I and II Regulated Chemicals |
|---|---|---|
| Alphabetical Order | Alphabetical Order | Alphabetical Order |
| Chronological Order | DEA Drug Code Number | DEA Number |
| CSA Schedule | List Number | |
| Illicit Uses and Threshold Quantities |
Exempted Lists
Exempt Anabolic Steroid Products
Exempt Anabolic Steroid Products Procedures
Exempt Anabolic Steroid Products List (PDF) (November 5, 2020)
Exempt Chemical Preparations
Exempt Chemical Preparations List (PDF) (April 23, 2021) For Application Dates Through December 31, 2020
Exempted Prescription Products
Exempted Prescription Products Application
Exempted Prescription Products List (PDF) (May 25, 2021)
Lists of Controlled Substances Disclaimer
Section 812 of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. §801 et seq.) (CSA) lists substances which were controlled in 1970 when the CSA was enacted. Since then many substances have been added, removed, or transferred from one schedule to another. The current list of controlled substances can be found in section 1308 of the most recent issue of Title 21 Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Part 1300 to end (21 CFR §1308) and the final rules which were published in the Federal Register subsequent to the issuance of the CFR.
These lists describe the basic or parent chemical and do not describe the salts, isomers, salts of isomers, esters, ethers, and derivatives which may be controlled substances. These are not comprehensive lists so please note that a substance need not be listed as a controlled substance to be treated as a scheduled substance for criminal prosecution. The 'Other Names' column, provides some examples of alternate names for certain compounds, and in some instances provides examples of 'positional isomers'. If outside parties want to ensure that a compound is not considered a scheduled substance or listed chemical, they should write the DEA, Drug and Chemical Evaluation Section (DRE), Diversion Control Division, 8701 Morrissette Drive, Springfield, Virginia 22152, for an official determination.
A substance (not included on these lists) may also be regulated as a controlled substance analogue. A controlled substance analogue is a substance which is intended for human consumption, is structurally substantially similar to a schedule I or schedule II substance, is pharmacologically substantially similar to a schedule I or schedule II substance, or is represented as being similar to a schedule I or schedule II substance and is not an approved medication in the United States. See 21 U.S.C. §802(32)(A) for the definition of a controlled substance analogue and 21 U.S.C. §813 for the schedule.
Defined Abbreviations
| Defined Abbreviation | Controlled Substance Analogue |
|---|---|
| 2C-B | 4-Bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine |
| 2C-T-7 | 2,5-Dimethoxy-4(n)-propylthiophenethylamine |
| BZP | N-Benzylpiperazine |
| DMT | Dimethyltryptamine |
| DOM | 4-Methyl-2,5-dimethoxyamphetamine |
| GBL | Gamma butyrolactone |
| GHB | Gamma hydroxybutyric acid, gamma hydroxybutyrate, 4-hydroxybutanoic acid, sodium oxybate |
| LAAM | Levo-alphacetylmethadol |
| LSD | Lysergic acid diethylamide, lysergide |
| MDA | 3,4-Methylenedioxyamphetamine |
| MDE | 3,4-Methylenedioxy-N-ethylamphetamine |
| MDMA | 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine |
| MPPP | 1-Methyl-4-phenyl-4-propionoxypiperidine |
| P2P | Phenyl-2-propanone, phenylacetone |
| PCC | 1-Piperidinocyclohexanecarbonitrile |
| PCE | N-Ethyl-1-phenylcyclohexylamine |
| PCH | 1-Phenylcyclohexylamine |
| PCP | 1-(1-Phenylcyclohexyl)piperidine, phencyclidine |
| PEPAP | 1-(2-Phenylethyl)-4-phenyl-4-acetoxypiperidine |
| PHP | 1-(1-Phenylcyclohexyl)pyrrolidine |
| SPA | (-)-1-Dimethylamino-1,2-diphenylethane |
| TCP | 1-[1-(2-Thienyl)cyclohexyl]piperidine |
| TCPy | 1-[1-(2-Thienyl)cyclohexyl]pyrrolidine |
| THC | Tetrahydrocannabinols |
| THG | Tetrahydrogestrinone |
Definition of Controlled Substance Schedules
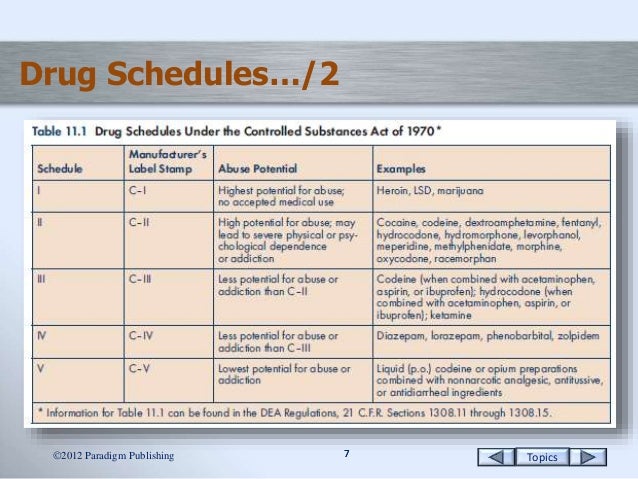
Drugs and other substances that are considered controlled substances under the Controlled Substances Act (CSA) are divided into five schedules. An updated and complete list of the schedules is published annually in Title 21 Code of Federal Regulations (C.F.R.) §§1308.11 through 1308.15. Substances are placed in their respective schedules based on whether they have a currently accepted medical use in treatment in the United States, their relative abuse potential, and likelihood of causing dependence when abused. Some examples of the drugs in each schedule are listed below.
Schedule I Controlled Substances
Substances in this schedule have no currently accepted medical use in the United States, a lack of accepted safety for use under medical supervision, and a high potential for abuse.
Some examples of substances listed in Schedule I are: heroin, lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), marijuana (cannabis), peyote, methaqualone, and 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine ('Ecstasy').
Schedule II/IIN Controlled Substances (2/2N)
Substances in this schedule have a high potential for abuse which may lead to severe psychological or physical dependence.
Examples of Schedule II narcotics include: hydromorphone (Dilaudid®), methadone (Dolophine®), meperidine (Demerol®), oxycodone (OxyContin®, Percocet®), and fentanyl (Sublimaze®, Duragesic®). Other Schedule II narcotics include: morphine, opium, codeine, and hydrocodone.
Examples of Schedule IIN stimulants include: amphetamine (Dexedrine®, Adderall®), methamphetamine (Desoxyn®), and methylphenidate (Ritalin®).
Other Schedule II substances include: amobarbital, glutethimide, and pentobarbital.
Schedule III/IIIN Controlled Substances (3/3N)
Substances in this schedule have a potential for abuse less than substances in Schedules I or II and abuse may lead to moderate or low physical dependence or high psychological dependence.
Examples of Schedule III narcotics include: products containing not more than 90 milligrams of codeine per dosage unit (Tylenol with Codeine®), and buprenorphine (Suboxone®).
Examples of Schedule IIIN non-narcotics include: benzphetamine (Didrex®), phendimetrazine, ketamine, and anabolic steroids such as Depo®-Testosterone.

Schedule IV Controlled Substances
Substances in this schedule have a low potential for abuse relative to substances in Schedule III.
Examples of Schedule IV substances include: alprazolam (Xanax®), carisoprodol (Soma®), clonazepam (Klonopin®), clorazepate (Tranxene®), diazepam (Valium®), lorazepam (Ativan®), midazolam (Versed®), temazepam (Restoril®), and triazolam (Halcion®).
Schedule V Controlled Substances
Schedule I, II, III, IV, & V Drugs | Drug Classifications ...
Substances in this schedule have a low potential for abuse relative to substances listed in Schedule IV and consist primarily of preparations containing limited quantities of certain narcotics.
Schedule 3 Veterinary Drugs List Australia
Examples of Schedule V substances include: cough preparations containing not more than 200 milligrams of codeine per 100 milliliters or per 100 grams (Robitussin AC®, Phenergan with Codeine®), and ezogabine.